Measurement While Drilling(MWD)
1, Introduction
In modern drilling operations, real-time data acquisition is essential for improving wellbore placement, optimizing performance, and ensuring safety. Measurement while Drilling(MWD) is a critical technology that enables real-time downhole measurements while the well is being drilled. MWD enhances directional drilling precision, facilitates geosteering, and provides essential information about the borehole environment, all without interrupting drilling progress.
2, What is MWD?
Measurement while drilling(MWD) refers to a set of tools and techniques integrated into the bottom-hole assembly(BHA) that continuously collect and transmit real-time data about the wellbore and formation conditions to the surface during drilling operations.
MWD primarily provides:
-Directional data(inclination, azimuth)
-Toolface orientation
-Downhole temperature and pressure
-Drilling dynamics(vibration, shock, torque)
-Basic formation evaluation(when combined with LWD)
MWD systems are often used in tandem with Logging While Drilling(LWD) tools, which focus more on formation properties.
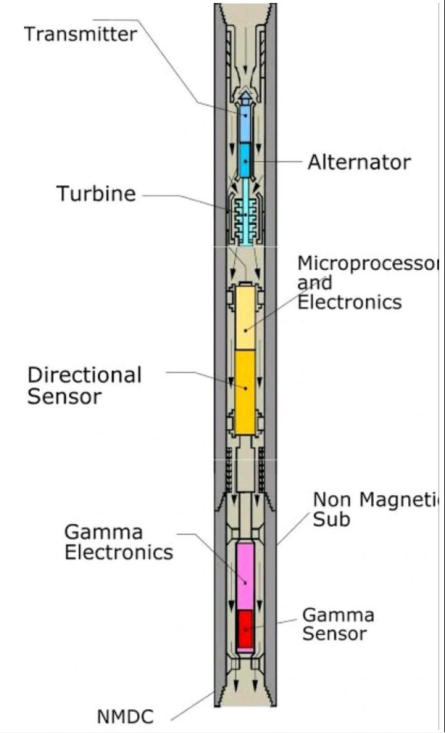
3, Key components of MWD systems
Component Function
Sensors measure inclination, azimuth, toolface, pressure, temperature, etc.
Telemetry system transmits data to the surface, usually via mud pulse, EM, or wired pipe Battery or Turbine power Powers downhole electronics.
Directional module contains gyroscopes, magnetometers, and accelerometers. Surface decoder interprets the signal received at the surface and displays data.

4, How MWD works
-Directional measurements
MWD tools use accelerometers and magnetometers to measure:
-Inclination: The deviation angle from vertical
-Azimuth: The compass direction of the wellbore
-Toolface angle: Orientation of the drilling tool(especially in motor-driven assemblies)
These measurements are vital for directional drilling and well trajectory control.
-Telemetry systems
Common methods include:
Telemetry type description
Mud pulse most widely used: encodes data as pressure pulses in the drilling mud.
Electromagnetic (EM) transmits signals through the formation using EM waves, faster but limited depth.
Wired pipe high-speed, high volume telemetry using cables inside drill pipe.